36X 2 9
36X 2 9 - The difference of squares can be factored using the rule: Use the quadratic formula to find the solutions. X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div:
Use the quadratic formula to find the solutions. The difference of squares can be factored using the rule: X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div:
Use the quadratic formula to find the solutions. The difference of squares can be factored using the rule: X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div:
Solved 9. Solve the linear congruence 36x 14 mod 38. 10.
The difference of squares can be factored using the rule: Use the quadratic formula to find the solutions. X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div:
Example 10 9x2 + 4y2 = 36, find foci, vertices, length
The difference of squares can be factored using the rule: X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: Use the quadratic formula to find the solutions.
If a polynomial 4X^44X^335X^2+36X9 has two zeroes as 3 and 3,find
The difference of squares can be factored using the rule: X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: Use the quadratic formula to find the solutions.
Solved 36. y=x22x3 38. yx + 6)+ 37 40, f(x)3x29x + 4
X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: Use the quadratic formula to find the solutions. The difference of squares can be factored using the rule:
Solved 36x^29y^224y16 [Math]
Use the quadratic formula to find the solutions. The difference of squares can be factored using the rule: X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div:
Example 10 9x2 + 4y2 = 36, find foci, vertices, length
X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: The difference of squares can be factored using the rule: Use the quadratic formula to find the solutions.
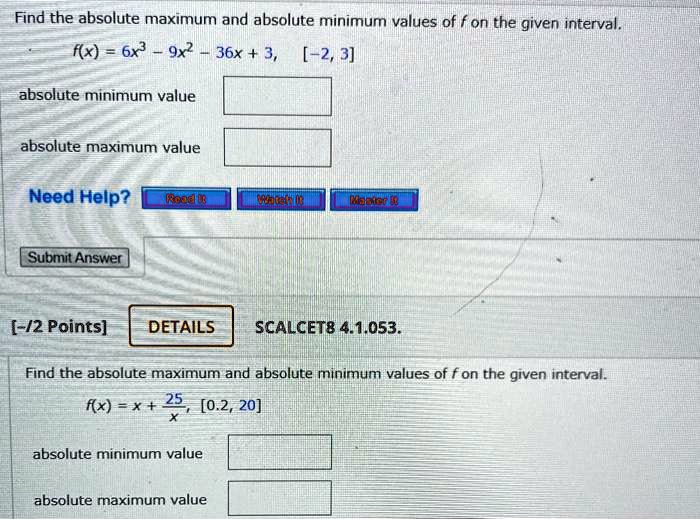
SOLVED Find the absolute maximum and absolute minimum values of f on
X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: The difference of squares can be factored using the rule: Use the quadratic formula to find the solutions.
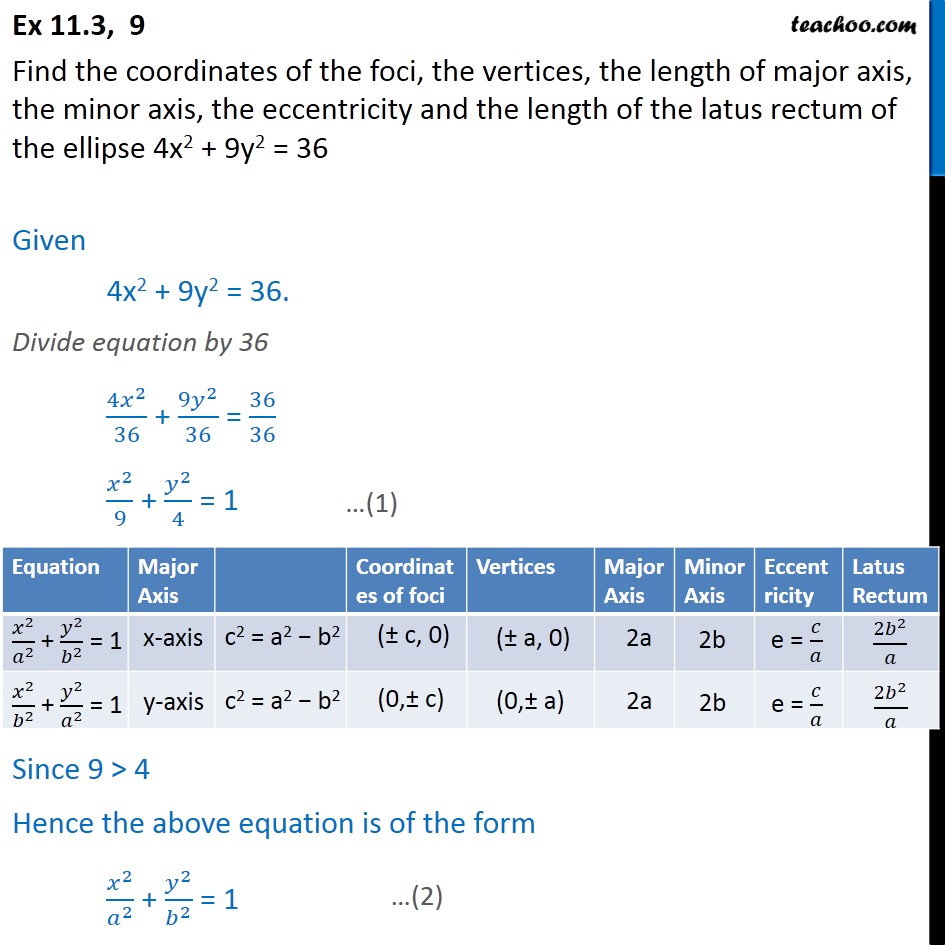
Ex 10.3, 9 4x2 + 9y2 = 36 Find length of major axis, minor
X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: Use the quadratic formula to find the solutions. The difference of squares can be factored using the rule:
Example 10 9x2 + 4y2 = 36, find foci, vertices, length
Use the quadratic formula to find the solutions. X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: The difference of squares can be factored using the rule:
The Difference Of Squares Can Be Factored Using The Rule:
Use the quadratic formula to find the solutions. X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: